
Joanne Blanchfield
The University of Queensland, Australia
Title: Glycosylation effects the bioavailability of sapanins in herbal extracts
Biography
Biography: Joanne Blanchfield
Abstract
Saponins are a class of natural product that are present in many herbal extracts. These compounds consist of a hydrophobic core, often a steroid or terpenoid derivative, decorated with varying numbers and types of sugar units attached at various positions. These compounds are often suggested to be the bioactive components of extracts but there is little known about the bioavailability of the compounds. Our group recently identified a new class of open-chain steroidal saponins from Chamaelirium luteum, an indigenous American herb marketed for “women’s issues”. We have fully characterised a series of these compounds and used the Caco-2 monolayer model of the GI tract to evaluate the potential bioavailability and metabolic vulnerability of eight of these compounds. The saponin, 6-Dehydrochamaeliroside A(1), was found to have good permeability and chamaeliroside A (2) was found to have moderate permeability. All bidesmodic saponins based on chiograsterol A and B cores exhibited low permeability. The aglycone steroids, chiograsterol B and helogenin, showed minimal bioavailability. None of the compounds appeared to be significantly metabolised by Caco-2 cell homogenate. Our results suggest an interesting structure activity relationship with the compounds with sugar units on one site of the core being absorbed while compounds with sugars at both ends of the core are not absorbed. We are further examining this relationship to determine if active transporters such as the GLUT transporters may be involved in the absorption of some saponins but not others. These results will also be presented in this talk.
Image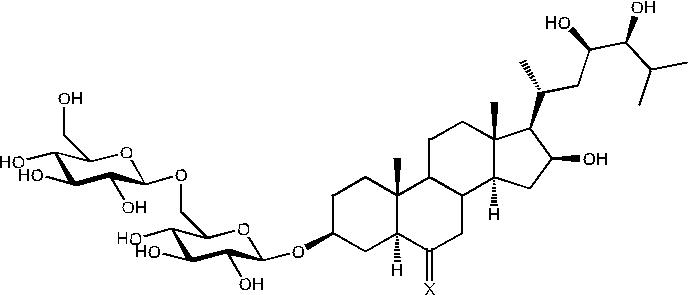
Figure 1: 6-Dehydrochamaeliroside A (1) X = O; Chamaeliroside A (2) X = H, OH.
References
1. Challinor, V.L., Parsons, P.G., Chap S., White, E.F., Blanchfield, J.T., Lehmann, R.P., De Voss, J.J. “Steroidal saponins from the roots of Smilax sp.: Structure and bioactivity.” Steroids, 77 (5), 504-511, 2012. DOI:10.1016/j.steroids.2012.01.009
2. Weaver, L.G.; Singh, Y.; Burn, P.L.; Blanchfield, J.T. “The synthesis and ring-opening metathesis polymerization of glycomonomers” RSC Advances, 2016, 6 (37), 31256-31264. DOI:10.1039/C5RA25732H
3. Dewi, A.S., Cheney, K.L., Urquhart, H.H., Blanchfield, J.T. Garson, M.J., “The sequestration of oxy‑polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the nudibranchs Miamira magnifica and Miamira miamirana” Marine Drugs, 2016, 14(11), 198
4. Weaver, L.G.; Singh, Y.; Vamvounis, G.; Wyatt, M.F.; Burn, P. L.; Blanchfield, J.T. –“Carbohydrate globules: molecular asterisk-cored dendrimers for carbohydrate presentation” Polymer Chemistry, 5(4), 1173-1179, 2014. DOI: 10.1039/ C3PY01123B.
5. Weaver, Lucy G.; Singh, Yogendra; Blanchfield, Joanne T.; Burn, Paul L. "A simple iterative method for the synthesis of â-(1®6)-glucosamine oligosaccharides.” Carbohydrate Research, 371, 68-76, 2013. DOI:10.1016/j.carres.2013.01.008
